To solve either (P) or (R), we take as our guiding philosophy:
do not discretize until (unless) necessary. In many cases, we
can actually characterize solutions to (P) and (R) by solving a
system of nonlinear equations in ![]() , which we can then solve
numerically.
, which we can then solve
numerically.
In short, our characterization is obtained by considering the dual problems:
![]()
and
![]()
where ![]() can be explicitly calculated, and
can be explicitly calculated, and ![]() .
.
For example, in maximum entropy problems, we begin with
![]()
with dual problem
![]()
To solve ![]() , we observe that
, we observe that ![]() is concave, and so a maximum occurs exactly
when
is concave, and so a maximum occurs exactly
when ![]() . That is, we solve
. That is, we solve ![]() for
for ![]() , which is a system of nonlinear equations:
, which is a system of nonlinear equations:
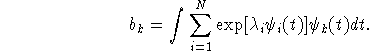
Once the optimal dual vector ![]() is obtained, we can recover
the optimal function
is obtained, we can recover
the optimal function ![]() from the formula
from the formula
![]()
when ![]() .
.
In the ME case, ![]() ,
, ![]() , so
the maximum entropy solution is given by
, so
the maximum entropy solution is given by
![]()
which is a functional form of the solution.